Reduction of Inflammation
Mesenchymal stem cells have anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce inflammation in damaged tissues of the shoulder, which can alleviate pain and stiffness.
Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC) Transplantation
Treatment of Rotator
Cuff Injury

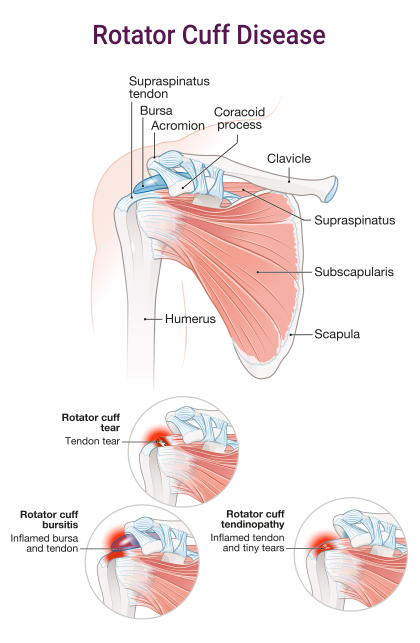

Rotator cuff tendinitis is a common injury in which the tendons of the rotator cuff, a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint, become inflamed and painful. Here are some things we know about this injury today:
Symptoms: Symptoms of rotator cuff tendinitis include shoulder pain, especially when lifting the arm overhead, arm weakness, difficulty sleeping on the affected side, and popping or snapping sensation in the shoulder joint.
Diagnosis: The diagnosis of rotator cuff tendinitis is made through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests such as X-ray or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Prevalence: The prevalence of rotator cuff tendinitis in the general population is estimated to be around 2-5%. However, this number increases significantly in older age groups, affecting up to 20% of individuals over 70 years old.
Laterality: Rotator cuff tendinitis can affect both the right and left shoulders, although some studies suggest that the dominant shoulder (usually the right in most people) has a higher predisposition to develop this injury.
The causes of rotator cuff tendinitis can vary, but they are generally attributed to a combination of factors. Some common causes include:
An acute injury, such as a fall or a direct blow, can damage the tendons of the rotator cuff and cause inflammation.
Rotator cuff tendinitis can also occur as a result of repetitive arm use in activities that involve lifting heavy objects, throwing, swimming, painting, or any activity that involves repetitive shoulder movements.
As we age, the tendons of the rotator cuff can weaken and lose elasticity, which increases the risk of tendinitis.
Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to develop rotator cuff tendinitis.
Chronic inflammation in the brain may play a role in the development of Parkinson's disease.
Poor posture can contribute to tension in the muscles and tendons of the shoulder, increasing the risk of tendinitis.
Certain diseases such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout can increase the risk of developing rotator cuff tendinitis.
Scientific research on the treatment of rotator cuff injury using mesenchymal stem cells is ongoing
Moravia, San José, Costa Rica.
